Bayes Theorem for conditional probability is applied to Oregon Health Authority COVID-19 reports to calculate the probability of death (Mortality Risk) given a positive infection test result. This same statistical method is commonly used in cancer and pre-employment drug screening. Latest data is available at OHA.
Executive Summary
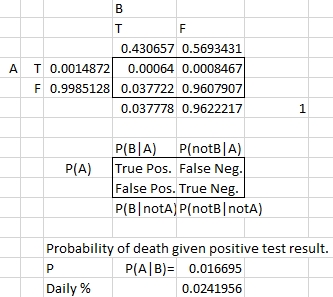
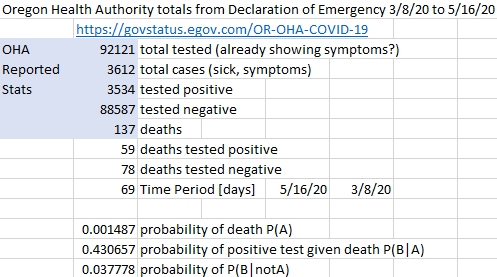
As of 5/16/20, In Oregon’s population of cases attributed to COVID-19 infection, the probability of death for those testing positive is estimated to be 1.67%. Strangely, more COVID-19 dead patients test negative (78) than positive (59). Also, the probability of false positive (3.77%) is relatively high compared to false negative (0.08%). This begs the question, are so many false positive deaths really due to the virus?
Bayesian Definitions

Empirical Data
Scarce testing resources may not accurately sample asymptomatic infections, in which case the mortality risk here is exaggerated.
Joint Probability Distribution